The Benefits of 4G GPS Trackers Over Older Technologies
4G GPS trackers have revolutionized how we monitor vehicles, assets, and even people, offering significant improvements over older technologies like 2G or 3G. As older networks phase out, 4G GPS trackers stand out for their speed, reliability, and advanced features. Whether used for fleet management, personal vehicle security, or tracking valuable equipment, these modern devices provide benefits that make them a smarter choice. Let’s explore why 4G GPS trackers outperform their predecessors.
1. Faster Data Transmission
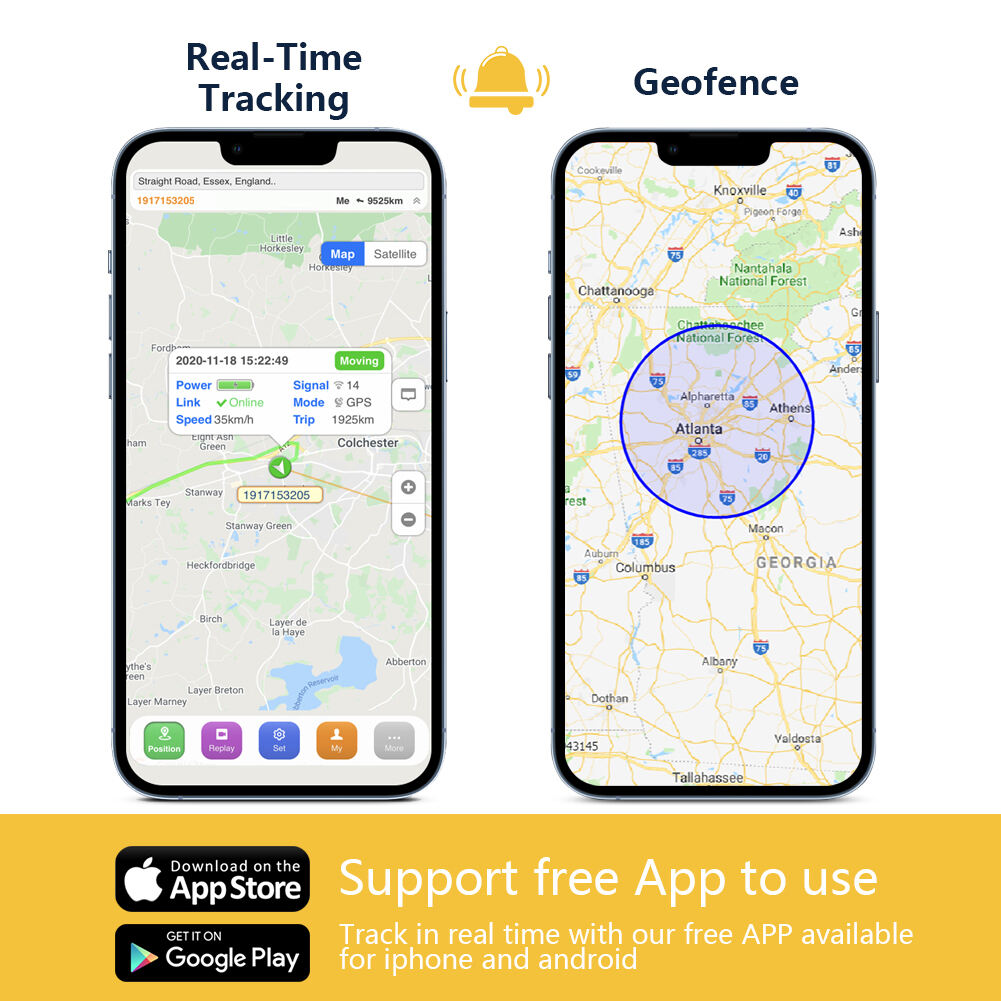
One of the biggest advantages of 4G GPS trackers is their ability to send and receive data much faster than older models. 2G and 3G trackers often delay updates, taking 30 seconds or more to share location info. 4G GPS trackers, by contrast, transmit data in real time—sometimes in under 5 seconds.
- Real-time tracking: For fleet managers, this means knowing exactly where a delivery truck is at any moment, allowing them to adjust routes instantly if there’s traffic or a delay.
- Quick alerts: If a vehicle is stolen or a driver speeds, 4G GPS trackers send alerts to your phone or computer immediately. Older trackers might take minutes to notify you, giving thieves more time to escape.
- Smoother updates: Faster data transmission ensures location points on a map are connected smoothly, showing a clear path of travel. With 2G, maps often have gaps or jumpy movements, making it hard to follow a vehicle’s route.
This speed is a game-changer for time-sensitive operations, like emergency services or same-day delivery.
2. Better Network Coverage
As telecom companies shut down 2G and 3G networks to make room for 4G and 5G, older trackers are losing coverage—especially in rural or remote areas. 4G GPS trackers, however, work on widely available 4G networks, ensuring reliable service almost everywhere.
- No dead zones: 4G networks cover more than 95% of populated areas in most countries, so 4G GPS trackers rarely lose signal. This is critical for trucks driving through rural regions or hikers using personal trackers.
- Future-proof: 4G networks will be supported for at least the next 10 years, while 2G/3G networks are already being phased out. Investing in 4G GPS trackers avoids the need to replace devices soon.
- Consistent performance: Even in busy cities, 4G networks handle more devices at once without slowing down. Older trackers often struggle in crowded areas, dropping signals when many people use the network.
For example, a construction company using 4G GPS trackers to monitor equipment in remote job sites can always check on their tools, whereas a 2G tracker might go offline for hours.
3. More Reliable in Poor Conditions
Older trackers often fail in bad weather or harsh environments, but 4G GPS trackers are built to handle tough conditions.
- Weather resistance: Many 4G GPS trackers have stronger, waterproof designs, working in rain, snow, or extreme temperatures (-40°F to 140°F). Older models might short-circuit in heavy rain.
- Better GPS accuracy: 4G GPS trackers use advanced chips that lock onto satellite signals faster and more reliably, even in areas with tall buildings or dense trees. This means location data is accurate to within 3–5 feet, compared to 10–20 feet with 2G.
- Battery efficiency: Despite faster data transmission, 4G GPS trackers often have longer battery life. They use power more efficiently, so a single charge can last weeks for asset trackers, compared to days with 2G devices.
This reliability makes 4G GPS trackers ideal for outdoor use, from tracking boats to monitoring farm equipment.

4. Advanced Features Not Possible with Older Tech
4G’s speed and capacity let 4G GPS trackers offer features that 2G/3G devices can’t handle:
- Video and audio: Some 4G GPS trackers include cameras or microphones, allowing live video streaming from inside a vehicle. This helps fleet managers check if drivers are distracted or if cargo is secure—something 2G trackers can’t do due to slow data speeds.
- Sensor integration: 4G GPS trackers connect to other sensors, like temperature monitors (for refrigerated trucks) or motion detectors (for assets). They can send detailed data, such as “the truck’s cargo hold is too warm,” in real time.
- Over-the-air updates: 4G GPS trackers can update their software wirelessly, adding new features or fixing bugs without needing to be physically connected to a computer. Older trackers often require manual updates, which are time-consuming.
- Geofencing with precision: Geofences (virtual boundaries) set on 4G GPS trackers are more accurate. You can create smaller zones (like a 50-foot radius around a store) and get alerts the second a vehicle enters or exits—older trackers might miss the boundary or delay the alert.
5. Cost-Effective in the Long Run
While 4G GPS trackers might cost slightly more upfront than older models, they save money over time:
- No need to replace soon: As 2G/3G networks shut down, users of older trackers will have to buy new devices anyway. Investing in 4G GPS trackers avoids this extra expense.
- Reduced operational costs: Faster alerts and better tracking help prevent theft, reduce fuel waste (by optimizing routes), and lower maintenance costs (by monitoring vehicle health). A fleet using 4G trackers might save thousands annually compared to using 2G.
- Fewer service interruptions: Older trackers often lose signal, requiring time and effort to troubleshoot. 4G GPS trackers’ reliable performance means less downtime and fewer headaches for managers.
6. Compatibility with Modern Systems
Most fleet management software and apps are designed for 4G GPS trackers. They integrate seamlessly, allowing users to manage trackers alongside other tools like invoicing or scheduling software. Older trackers often struggle to connect with new systems, leading to data silos and inefficiency.
For example, a delivery company using 4G GPS trackers can automatically sync delivery times with their customer app, letting clients see exactly when their package will arrive. This level of integration is nearly impossible with 2G technology.
FAQ
Will 2G GPS trackers stop working soon?
Yes. Many countries (like the US, EU, and Australia) are shutting down 2G networks by 2025. After that, 2G trackers will lose coverage and stop working.
Do 4G GPS trackers work in areas with no 4G?
They can switch to 3G as a backup in some cases, but 3G networks are also being phased out. For remote areas, look for 4G GPS trackers with satellite connectivity as a fallback.
Are 4G GPS trackers harder to install than older models?
No, most are just as easy. Many plug into a vehicle’s OBD-II port, while asset trackers are small and battery-powered—no technical skills needed.
Can 4G GPS trackers be used for personal vehicles, not just fleets?
Absolutely. They’re great for tracking family cars, especially for parents monitoring teen drivers or owners protecting against theft.
Do 4G GPS trackers use more data than older models?
They can, but data plans for 4G trackers are affordable. Most providers offer plans with enough data for daily tracking (location updates, alerts) for $5–$15 per month.
Is 5G better than 4G for GPS trackers?
5G is faster, but 4G is still more widely available. Most 4G GPS trackers work well, and 5G trackers are often unnecessary unless you need ultra-fast video streaming.
Table of Contents
- The Benefits of 4G GPS Trackers Over Older Technologies
- 1. Faster Data Transmission
- 2. Better Network Coverage
- 3. More Reliable in Poor Conditions
- 4. Advanced Features Not Possible with Older Tech
- 5. Cost-Effective in the Long Run
- 6. Compatibility with Modern Systems
-
FAQ
- Will 2G GPS trackers stop working soon?
- Do 4G GPS trackers work in areas with no 4G?
- Are 4G GPS trackers harder to install than older models?
- Can 4G GPS trackers be used for personal vehicles, not just fleets?
- Do 4G GPS trackers use more data than older models?
- Is 5G better than 4G for GPS trackers?